|
Overview
Approximately 75% of us present with one leg longer than the other. It?s staggering, literally, that so many people walk about with an imbalance. Yet to have one leg longer than the other doesn?t seem to create pain for everyone but for those that it does it brings pain in a myriad of dysfunction from TMJ, headaches, low back pain, IBS, bladder problems, sexual dysfunction, sacroiliac joint pain, pubis dysfunction, groin strain, gluteal dysfunction as well as the formation of trigger points. 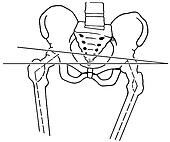 Causes A patient?s legs may be different lengths for a number of reasons, including a broken leg bone may heal in a shorter position, particularly if the injury was severe. In children, broken bones may grow faster for a few years after they heal, resulting in one longer leg. If the break was near the growth center, slower growth may ensue. Children, especially infants, who have a bone infection during a growth spurt may have a greater discrepancy. Inflammation of joints, such as juvenile arthritis during growth, may cause unequal leg length. Compensation for spinal or pelvic scoliosis. Bone diseases such as Ollier disease, neurofibromatosis, or multiple hereditary exostoses. Congenital differences. Symptoms The patient/athlete may present with an altered gait (such as limping) and/or scoliosis and/or low back pain. Lower extremity disorders are possibly associated with LLD, some of these are increased hip pain and degeneration (especially involving the long leg). Increased risk of: knee injury, ITB syndrome, pronation and plantar fascitis, asymmetrical strength in lower extremity. Increased disc or vertebral degeneration. Symptoms vary between patients, some patients may complain of just headaches. Diagnosis The only way to decipher between anatomical and functional leg length inequalities (you can have both) is by a physical measurement and series of biomechanical tests. It is actually a simple process and gets to the true cause of some runner?s chronic foot, knee, hip and back pain. After the muscles are tested and the legs are measured it may be necessary to get a special X-ray that measures both of your thighs (Femurs) and legs (Tibias). The X-ray is read by a medical radiologist who provides a report of the actual difference down to the micrometer leaving zero room for error. Once the difference in leg length is known, the solution becomes clear. Non Surgical Treatment Whether or not treatment should be pursued depends on the amount of discrepancy. In general, no treatment (other than a heel life, if desired) should be considered for discrepancies under two centimeters. If the discrepancy measures between two and five centimeters, one might consider a procedure to equalize leg length. Usually, this would involve closure of the growth plate on the long side, thereby allowing the short side to catch up; shortening the long leg; or possibly lengthening the short leg.  increase height quickly Surgical Treatment Large leg length inequalities can be treated by staged lengthenings or by simultaneous ipsilateral femoral and tibial lengthenings. Additionally, lengthenings can be combined with appropriately timed epiphysiodesis in an effort to produce leg length equality. Staged lengthenings are often used for congenital deficiencies such as fibular hemimelia, in which 15 cm or more may be needed to produce leg length equality. We typically plan for the final lengthening to be completed by age 13 or 14 years, and allow at least 3 years between lengthenings. Lengthening of both the tibia and femur simultaneously requires aggressive therapy and treatment of soft tissue contractures. Curran et al[57] reported the need for surgical release of soft tissue contractures in 3 of 8 patients treated with simultaneous ipsilateral femoral and tibial lengthenings. Lengthening over an IM nail can be done in an effort to decrease the amount of time the fixator needs to be worn and to prevent angular malalignment. This technique requires that the patient be skeletally mature and it carries a higher risk of osteomyelitis (up to 15%). Additionally, if premature consolidation occurs, a repeat corticotomy is more difficult. Overview
 Heel pain is a very challenging problem as it can be local and/or referred. It has been more prevalent recently due to the hard grounds on which people have to run. Commonly people will present with heel pain, thrusting an x-ray at you, and being adamant that the problem is a ?heel spur?. This is defined as a small bone that grows from the heel, directing forwards towards the toes. This may be as small as 1 mm to anything as large as 8 - 10 mm. Most of the time, this is an incidental finding, as there many heels that are pain free that have heel spurs evident on x-rays. The spur is thought to be a result of traction of the plantar fascia on the heel. In some cases, the spur may contribute to the symptoms, but is not the main cause. This should be explained very carefully to the patient, as the focus on the spur may limit the recovery, as the patient may believe that the only way to eliminate the pain is to remove the spur. Causes If it hurts under your heel, you may have one or more conditions that inflame the tissues on the bottom of your foot. When you step on a hard object such as a rock or stone, you can bruise the fat pad on the underside of your heel. It may or may not look discolored. The pain goes away gradually with rest. Doing too much running or jumping can inflame the tissue band (fascia) connecting the heel bone to the base of the toes. The pain is centered under your heel and may be mild at first but flares up when you take your first steps after resting overnight. You may need to do special exercises, take medication to reduce swelling and wear a heel pad in your shoe. When plantar fasciitis continues for a long time, a heel spur (calcium deposit) may form where the fascia tissue band connects to your heel bone. Your doctor may take an X-ray to see the bony protrusion. Treatment is usually the same as for plantar fasciitis: rest until the pain subsides, do special stretching exercises and wear heel pad shoe inserts. Having a heel spur may not cause pain and should not be operated on unless symptoms become chronic. Symptoms See your doctor immediately if you have Severe pain and swelling near your heel. Inability to bend your foot downward, rise on your toes or walk normally. Heel pain with fever, numbness or tingling in your heel. Severe heel pain immediately after an injury. Schedule an office visit if you have. Heel pain that continues when you're not walking or standing. Heel pain that lasts more than a few weeks, even after you've tried rest, ice and other home treatments. Diagnosis After you have described your foot symptoms, your doctor will want to know more details about your pain, your medical history and lifestyle, including. Whether your pain is worse at specific times of the day or after specific activities. Any recent injury to the area. Your medical and orthopedic history, especially any history of diabetes, arthritis or injury to your foot or leg. Your age and occupation. Your recreational activities, including sports and exercise programs. The type of shoes you usually wear, how well they fit, and how frequently you buy a new pair. Your doctor will examine you, including. An evaluation of your gait. While you are barefoot, your doctor will ask you to stand still and to walk in order to evaluate how your foot moves as you walk. An examination of your feet. Your doctor may compare your feet for any differences between them. Then your doctor may examine your painful foot for signs of tenderness, swelling, discoloration, muscle weakness and decreased range of motion. A neurological examination. The nerves and muscles may be evaluated by checking strength, sensation and reflexes. In addition to examining you, your health care professional may want to examine your shoes. Signs of excessive wear in certain parts of a shoe can provide valuable clues to problems in the way you walk and poor bone alignment. Depending on the results of your physical examination, you may need foot X-rays or other diagnostic tests. Non Surgical Treatment When consulting a doctor about heel pain, a patient can expect to be questioned about their level of pain, how long they?ve been experiencing it, and which activities aggravate or alleviate the condition. The doctor may order x-rays, a physical therapy regimen, or refer the afflicted individual to an orthopedic specialist for further examination. The doctor may attempt to recreate conditions that cause the heel pain to flare up in order to study reaction and cause in the patient, but this will be temporary and the doctor will stop this test at the request of the patient. A patient with heel pain may also be fitted with special inserts for their shoes to help correct arch and heel problems that cause pain. Heel problems can range from the mildly irritating to the nearly devastating, but proper prevention in care will help keep each step pain free. Advanced orthopedics, pain management, and technologically-honed surgical techniques ensure that no patient needs to suffer with the discomfort of heel pain and the restrictions it imposes on an active lifestyle. Surgical Treatment Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (EST) is a fairly new type of non-invasive treatment. Non-invasive means it does not involve making cuts into your body. EST involves using a device to deliver high-energy soundwaves into your heel. The soundwaves can sometimes cause pain, so a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your heel. It is claimed that EST works in two ways. It is thought to have a "numbing" effect on the nerves that transmit pain signals to your brain, help stimulate and speed up the healing process. However, these claims have not yet been definitively proven. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance about the use of EST for treating plantar fasciitis. NICE states there are no concerns over the safety of EST, but there are uncertainties about how effective the procedure is for treating heel pain. Some studies have reported that EST is more effective than surgery and other non-surgical treatments, while other studies found the procedure to be no better than a placebo (sham treatment). bestshoelifts Prevention  A variety of steps can be taken to avoid heel pain and accompanying afflictions. Wear shoes that fit well-front, back, and sides-and have shock-absorbent soles, rigid shanks, and supportive heel counters. Wear the proper shoes for each activity. Do not wear shoes with excessive wear on heels or soles. Prepare properly before exercising. Warm up and do stretching exercises before and after running. Pace yourself when you participate in athletic activities. Don't underestimate your body's need for rest and good nutrition. If obese, lose weight. Overview
 Morton neuromas are focal areas of symptomatic perineural fibrosis around a plantar digital nerve of the foot. The abnormality is non-neoplastic and does not represent a true neuroma. It may more correctly be known as Morton?s metatarsalgia. The condition is thought to be due to chronic entrapment of the nerve by the intermetatarsal ligament. It most often occurs in middle-aged individuals and is many times more common in women than men. Approximately 30% of asymptomatic middle-aged persons have the radiological pathologic findings of a Morton?s neuroma. Morton neuromas are focal areas of symptomatic perineural fibrosis around a plantar digital nerve of the foot. The abnormality is non-neoplastic and does not represent a true neuroma. It may more correctly be known as Morton?s metatarsalgia. The condition is thought to be due to chronic entrapment of the nerve by the intermetatarsal ligament. It most often occurs in middle-aged individuals and is many times more common in women than men. Approximately 30% of asymptomatic middle-aged persons have the radiological pathologic findings of a Morton?s neuroma.Causes Morton's neuroma develops for several reasons. The primary reason is wearing narrow toe-box shoes, which compress the metatarsal heads. Certain anatomical factors also make nerve compression more likely with the narrow toe box shoes. In some people fibers, the medial and lateral plantar nerves converge close to the heads of the third and fourth metatarsals. This junction creates a larger nerve structure between the metatarsal heads making it more vulnerable to compression. Symptoms What are the symptoms of Morton?s neuroma? A sharp or stinging pain between the toes when standing or walking. Pain in the forefoot between the toes. Swelling between the toes. Tingling (?pins and needles?) and numbness. Feeling like there is a ?bunched up sock? or a pebble or marble under the ball of the foot. Diagnosis There is a special orthopedic test called the Morton's test that is often used to evaluate the likelihood of plantar nerve compression. For this test, the client is supine on the treatment table. The practitioner grasps the client's forefoot from both sides and applies moderate pressure, squeezing the metatarsal heads together. If this action reproduces the client's symptoms (primarily sharp, shooting pain into the toes, especially the third and fourth), Morton's neuroma may exist. Non Surgical Treatment Orthotics and corticosteroid injections are widely used conservative treatments for Morton?s neuroma. In addition to traditional orthotic arch supports, a small foam or fabric pad may be positioned under the space between the two affected metatarsals, immediately behind the bone ends. This pad helps to splay the metatarsal bones and create more space for the nerve so as to relieve pressure and irritation. It may however also elicit mild uncomfortable sensations of its own, such as the feeling of having an awkward object under one's foot. Corticosteroid injections can relieve inflammation in some patients and help to end the symptoms. For some patients, however, the inflammation and pain recur after some weeks or months, and corticosteroids can only be used a limited number of times because they cause progressive degeneration of ligamentous and tendinous tissues.  Surgical Treatment If your pain continues despite several months of conservative treatment, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the neuroma or to widen the space through which the affected nerve travels. These types of surgery often are done under local anesthesia. If your doctor removes a portion of the affected nerve along with the neuroma, you may develop permanent numbness between the toes. There are actually two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital implies you are born with it. One leg is structurally shorter compared to the other. Through developmental periods of aging, the human brain senses the walking pattern and recognizes some variance. The entire body typically adapts by dipping one shoulder over to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch is not very uncommon, doesn't need Shoe Lifts to compensate and usually doesn't have a serious effect over a lifetime.
 Leg length inequality goes typically undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this problem is simply corrected, and can eliminate a number of incidents of lumbar pain. Therapy for leg length inequality usually involves Shoe Lifts. These are typically low-priced, in most cases costing under twenty dollars, compared to a custom orthotic of $200 or maybe more. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position. Mid back pain is the most widespread condition impacting people today. Around 80 million men and women experience back pain at some stage in their life. It's a problem that costs employers millions of dollars every year due to time lost and productivity. Fresh and superior treatment solutions are always sought after in the hope of decreasing the economic impact this issue causes.  People from all corners of the earth suffer the pain of foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In these types of situations Shoe Lifts might be of very useful. The lifts are capable of relieving any pain in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by numerous certified orthopaedic practitioners". In order to support the human body in a nicely balanced fashion, the feet have a critical part to play. Inspite of that, it is often the most neglected area in the human body. Some people have flat-feet meaning there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This causes other body parts like knees, ankles and backs to be affected too. Shoe Lifts make sure that appropriate posture and balance are restored.  Overview OverviewThere are two types of Hammertoe, Flexible hammertoes. If the toe still can be moved at the joint, it's a flexible hammertoe. That's good, because this is an earlier, milder form of the problem. There may be several treatment options. Rigid hammertoes. If the tendons in the toe become rigid, they press the joint out of alignment. At this stage, the toe can't be moved. It usually means that surgery is needed. Causes Footwear can contribute significantly to the development of hammertoes. Shoes that are too small force your toes into a curled position. Over time, your toe tendons adjust to this positioning, causing your toe or toes to hold a hammered shape. Athletes may be especially susceptible, because of the increased forces on the toes from shoes that are too small or tight. Heel elevation in footwear is also problematic, as it causes your toes to be pushed into the shoe?s toe box. Heel elevation additionally contributes to muscle imbalance. A common example of this is when your Achilles tendon-the tendon at the back of your leg that attaches your calf muscles to your heel bone-is too tight, causing the tendons on the top of your foot that attach to your toes to work too hard and hold your toes in an unnatural, elevated position.  Symptoms Hammertoe and mallet toe feature an abnormal bend in the joints of one or more of your toes. Moving the affected toe may be difficult or painful. Corns and calluses can result from the toe rubbing against the inside of your shoes. See your doctor if you have persistent foot pain that affects your ability to walk properly. Diagnosis Hammertoes are progressive, they don?t go away by themselves and usually they will get worse over time. However, not all cases are alike, some hammertoes progress more rapidly than others. Once your foot and ankle surgeon has evaluated your hammertoes, a treatment plan can be developed that is suited to your needs. Non Surgical Treatment Conservative treatment starts with new shoes that have soft, roomy toe boxes. Shoes should be one-half inch longer than your longest toe. (Note: For many people, the second toe is longer than the big toe.) Avoid wearing tight, narrow, high-heeled shoes. You may also be able to find a shoe with a deep toe box that accommodates the hammer toe. Or, a shoe specialist (Pedorthist) may be able to stretch the toe box so that it bulges out around the toe. Sandals may help, as long as they do not pinch or rub other areas of the foot. Surgical Treatment Treatment of a severe hammertoe that has become rigid includes surgery. What is done during the surgery depends on how misshapen and inflexible the toe is. The surgeon may make a cut over your toe and release the tendon by cutting the tendon away from the bone. The surgeon may remove a small piece of bone from the toe. The surgeon may realign the tendons to reposition your toe or fasten the bones with pins. Sometimes the surgeon may have to join the bones in the toe. In this case, you will no longer be able to bend the toe, but the toe will be flat.  Prevention Certain exercises such as moving and stretching your toe gently with your hands and picking up small or soft objects such as marbles or towels can keep your toe joints flexible, simple exercises can stretch and strengthen your muscles. Limit high-heel use, well-designed flat shoes will be more comfortable than high heels. Don't wear shoes that are too short or too narrow, or too shallow, this is especially important for children going through periods of rapid growth, the toe area should be high enough so that it doesn't rub against the top of your toes.
Overview
 What most people call a bunion is actually known as "Hallux valgus". Hallux valgus refers to the condition in which the big toe is angled excessively towards the second toe and a bunion is a symptom of the deformity. In a normal foot, the big toe and the long bone that leads up to it (the first metatarsal) are in a straight line. However, Hallux valgus occurs when the long foot bone veers towards your other foot and your big toes drifts towards your second toe. A bunion actually refers to the bony prominence on the side of the big toe. This can also form a large sac of fluid, known as a bursa, which can then become inflamed and sore. What most people call a bunion is actually known as "Hallux valgus". Hallux valgus refers to the condition in which the big toe is angled excessively towards the second toe and a bunion is a symptom of the deformity. In a normal foot, the big toe and the long bone that leads up to it (the first metatarsal) are in a straight line. However, Hallux valgus occurs when the long foot bone veers towards your other foot and your big toes drifts towards your second toe. A bunion actually refers to the bony prominence on the side of the big toe. This can also form a large sac of fluid, known as a bursa, which can then become inflamed and sore.Causes Bunions are most often caused by an inherited faulty mechanical structure of the foot. It is not the bunion itself that is inherited, but certain foot types that make a person prone to developing a bunion. Although wearing shoes that crowd the toes won?t actually cause bunions, it sometimes makes the deformity get progressively worse. Symptoms may therefore appear sooner. Symptoms Red, thickened skin along the inside edge of the big toe. A bony bump at this site. Pain over the joint, which pressure from shoes makes worse. Big toe turned toward the other toes and may cross over the second toe. Diagnosis Most patients are diagnosed to have bunions from clinical history and examination. However, in some cases, X-rays will be performed to determine the extent of damage to the joint. Furthermore, it will enable the treating doctor to decide on the best course of management of the patient. Non Surgical Treatment Treatment of hallux valgus nearly always starts with adapting shoe wear to fit the foot. In the early stages of hallux valgus, converting from a shoe with a pointed toe to a shoe with a wide forefoot (or toe box) may arrest the progression of the deformity. Since the pain that arises from the bunion is due to pressure from the shoe, treatment focuses on removing the pressure that the shoe exerts on the deformity. Wider shoes reduce the pressure on the bunion. Bunion pads may reduce pressure and rubbing from the shoe. There are also numerous devices, such as toe spacers, that attempt to splint the big toe and reverse the deforming forces.  Surgical Treatment Recent advances in surgical techniques have led to very high success rates for bunion surgery. In most cases the patient can walk immediately after surgery without crutches. As well most patients find the surgery to be virtually pain free. Almost all bunion surgery is done as an outpatient at a surgery center. Most bunion surgery is performed with a local anesthetic block and IV sedation (twilight sleep). After the procedure you will be moved to the recovery room for about an hour. You will then be ready to go home. Prevention Shoes that possess tapering toe boxes should be avoided if you have a bunion, as narrow toe boxes will hasten the progression of your bunion deformity. In some cases, conservative measures, including switching to appropriate footwear, may not have the desired effect, and your podiatrist may recommend for you a surgical procedure known as a bunionectomy. Overview
Pronation is the inward movement of the foot as it rolls to distribute the force of impact of the ground as you run. The foot "rolls" inward about fifteen percent, comes in complete contact with the ground, and can support your body weight without any problem. Pronation is critical to proper shock absorption, and it helps you push off evenly from the front of the foot. Although pronation is a natural movement of the foot, the size of the arch can affect its ability to roll, causing either supination (underpronation) or overpronation. If you have a normal arch, you're likely a normal pronator, meaning you'll do best in a shoe that offers moderate pronation control. People with flat feet normally overpronate, so they do well in a motion-control shoe that controls pronation. High-arched people typically underpronate, so they do best in a neutral-cushioned shoe that encourages a more natural foot motion.  Causes Flat feet don't automatically mean you have a problem. The problem can be divided into a flexible flat foot or rigid flat foot. The rigid flat foot is one that does not change shape when the foot becomes weight bearing. i.e. it does not go through the excessive motion of pronation. Generally speaking this foot does not provide too many problems. The flexible flat foot is the type that when it becomes weight bearing the foot and ankle tends to roll in (pronates) too far. This type of person will often say I have great arches but when I stand up much of this arch disappears as the foot excessively pronates When the foot is excessively pronating and causing problems like sore ankles, feet or knees when standing or exercising then arch support is extremely important to restore the foot structure. Symptoms Because overpronation affects the entire lower leg, many injuries and conditions may develop and eventually cause problems not only in the leg and foot, but also the knee, hips and lower back. Pain often begins in the arch of the foot or the ankle. Blisters may develop on the instep, or on the inside edge of the heels. As overpronation continues and problems develop, pain will be felt elsewhere, depending on the injury. Diagnosis So, how can you tell if you have overpronation, or abnormal motion in your feet, and what plantar fasciitis treatment will work to correct it? Look at your feet. While standing, do you clearly see the arch on the inside of your foot? If not, and if the innermost part of your sole touches the floor, then your feet are overpronated. Look at your (running/walking) shoes. If your shoes are more worn on the inside of the sole in particular, then pronation may be a problem for you. Use the wet foot test. Wet your feet and walk along a section of pavement, then look at the footprints you leave behind. A normal foot will leave a print of the heel connected to the forefoot by a strip approximately half the width of the foot on the outside of the sole. If you?re feet are pronated there may be little distinction between the rear and forefoot.  Non Surgical Treatment Solutions typically presented will include physical therapy sessions, prolonged prescription drug regimens, occasionally non-traditional approaches like holistic medicine and acupuncture. These options can provide symptom relief in the short term for some patients. However, these treatment methods cannot correct the internal osseous misalignment. Ligaments are not effective in limiting the motion of the ankle bone when excessive joint motion is present. Furthermore, there is not a single, specific ligament that is "too tight" that needs to be "stretched out." The muscles supporting the bones are already being "over-worked" and they cannot be strengthened enough to realign these bones. There is no evidence to suggest that any of these measures are effective in re-establishing or maintaining the normal joint alignment and function. Surgical Treatment Hyperpronation can only be properly corrected by internally stabilizing the ankle bone on the hindfoot bones. Several options are available. Extra-Osseous TaloTarsal Stabilization (EOTTS) There are two types of EOTTS procedures. Both are minimally invasive with no cutting or screwing into bone, and therefore have relatively short recovery times. Both are fully reversible should complications arise, such as intolerance to the correction or prolonged pain. However, the risks/benefits and potential candidates vary. Subtalar Arthroereisis. An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer. HyProCure Implant. A stent is placed into a naturally occurring space between the ankle bone and the heel bone/midfoot bone. The stent realigns the surfaces of the bones, allowing normal joint function. Generally tolerated in both pediatric and adult patients, with or without adjunct soft tissue procedures. Reported removal rates, published in scientific journals vary from 1%-6%. Overview
Sever's disease or calcaneal apophysitis heel pain is a common problem with children between the ages of 8 to 13 years. It has usually been more common in boys, but with the increase of girls in athletic activities, both sexes are having equal symptoms. A high percentage of these children have tight achilles tendons and hamstrings. This condition may occur in the foot with normal arch height or flat or pronated foot, but can be especially painful in the high arch foot. Causes Apart from the age of the young person, other factors that may contribute to developing the disease may include; overuse or too much physical activity. Your child?s heel pain may be caused by repeated stress on the heels (running and jumping activities), pressure on the back of the heel from too much standing or wearing poor-fitting shoes. This includes shoes that do not support or provide enough padding for your child?s feet. Symptoms On examination, the typical signs are tenderness on palpation of the heel, particularly on deep palpation at the Achilles tendon insertion. Pain on dorsiflexion of the ankle, particularly when doing active toe raises; forced dorsiflexion of the ankle is also uncomfortable. Swelling of the heel, usually mild. Calcaneal enlargement, in long-standing cases. Diagnosis It is not difficult for a doctor to diagnose Sever's disease in a youngster or teenager. A personal history and a physical examination are usually all it takes to determine the cause of heel pain. Non Surgical Treatment Your child may need to change or stop doing the activities that cause pain until the growth plate heals. Your child needs to wear shoes with good padding in the heels and good arch support. Special shoes or shoe inserts may help. Pain from Sever's disease may last weeks to months. The pain may come back if your child returns to sports or strenuous activities too soon. Prevention Sever's disease may be prevented by maintaining good joint and muscle flexibility in the years leading up to, and during, their growth spurts (eg girls 8 to 10, boys 10 to 12). Foot arch problems such as flat feet should be addressed after the age of five if they don't appear to be self-correcting. If you are concerned, please ask your health practitioner. The most important factor is the amount of weight-bearing exercise your child is currently performing. Finally, LISTEN To Your Child! If your child is suffering heel pain between the ages of 8 to 12, suspect Sever's disease until proven otherwise. Seek the professional opinion of your foot practitioner regarding its diagnosis and subsequent management.
Overview
 About two thirds of all Achilles tendon ruptures occur during sports. Total ruptures are most common in sports with stop-and-go movements, especially ball sports. The majority of patients suffered a ruptured Achilles tendon when stopping suddenly during a fast vigorous movement. Usually the Achilles tendon tears about 5 cm before it inserts into the heel bone. Particularly at risk for a tear are athletes who have already suffered from Achilles tendon problems for some time. About two thirds of all Achilles tendon ruptures occur during sports. Total ruptures are most common in sports with stop-and-go movements, especially ball sports. The majority of patients suffered a ruptured Achilles tendon when stopping suddenly during a fast vigorous movement. Usually the Achilles tendon tears about 5 cm before it inserts into the heel bone. Particularly at risk for a tear are athletes who have already suffered from Achilles tendon problems for some time.Causes The tendon is susceptible to injury and can rupture during vigorous activities such as running and jumping. Rupture can also occur as a result of gradual wear. After becoming chronically weakened, it can rupture during non-stress activities like walking. Symptoms Symptoms of an Achilles tendon injury are as follows. Pain along the back of your foot and above your heel, especially when stretching your ankle or standing on your toes; with tendinitis, pain may be mild and worsen gradually. If you rupture the tendon, pain can be abrupt and severe. Tenderness. Swelling. Stiffness. Hearing a snapping or popping noise during the injury. Difficulty flexing your foot or pointing your toes (in complete tears of the tendon). Diagnosis The diagnosis of an Achilles tendon rupture can be made easily by an orthopedic surgeon. The defect in the tendon is easy to see and to palpate. No x-ray, MRI or other tests are necessary. Non Surgical Treatment The most widely used method of non-surgical treatment involves the use of serial casting with gradual progression from plantar flexion to neutral or using a solid removable boot with heel inserts to bring the ends of the tendon closer together. The advantage of a solid removable boot is that it allows the patient to begin early motion and is removable. Wide variability exists among surgeons in regards to the period of absolute immobilization, initiating range of motion exercises, and progression of weight bearing status.  Surgical Treatment In general, Achilles tendon repair surgery has a much higher success rate and lower incidences of re-rupture than non-surgical methods of treatment. It is preferred by the nation?s leading athletes as the best course of action, allowing them to return to previous activity and performance levels at a much faster rate, with a lower chance or re-injury and less potential muscle loss. Prevention To help reduce your chance of getting Achilles tendon rupture, take the following steps. Do warm-up exercises before an activity and cool down exercises after an activity. Wear proper footwear. Maintain a healthy weight. Rest if you feel pain during an activity. Change your routine. Switch between high-impact activities and low-impact activities. Strengthen your calf muscle with exercises. |
|
